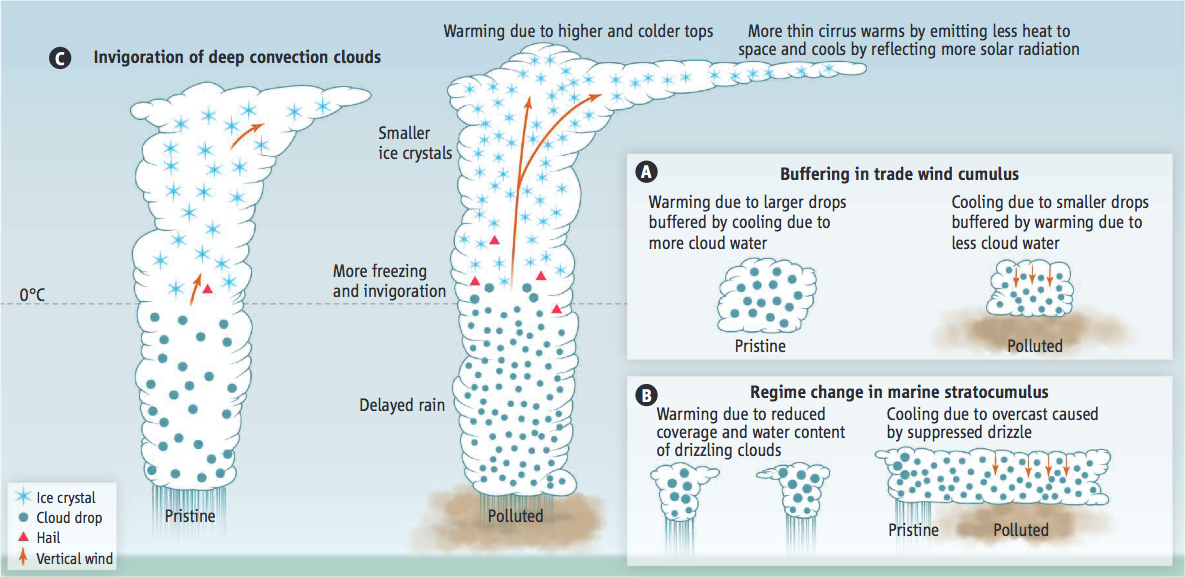
How aerosols affect the radiative properties of clouds.
By nucleating a larger
number of smaller cloud drops, aerosols affect cloud radiative forcing in various
ways. (
A
) Buffering in nonprecipitating clouds. The smaller drops evaporate faster
and cause more mixing of ambient air into the cloud top, which further enhances
evaporation. (
B
) Strong cooling. Pristine cloud cover breaks up by losing water to
rain that further cleanses the air in a positive feedback loop. Aerosols
suppressing precipitation prevent the breakup. (
C
) Larger and longer-lasting cirrus clouds.
By delaying precipitation, aerosols can invigorate deep convective clouds and
cause colder cloud tops that emit less thermal radiation. The smaller ice particles
induced by the pollution aerosols precipitate more slowly from the anvils. This can
cause larger and longer-lasting cirrus clouds, with opposite effects in the thermal
and solar radiation. The net effect depends on the relative magnitudes
Get the full article here.